Can Inflamed Nerves Trigger Arthritis Pain? Here's What You Need to Know
Imagine waking up one day, feeling unfamiliar sharp pains in your joints. As you attempt to pinpoint the source of this discomfort, it dawns on you that your nerves might be leading a revolt in your body. Could it be that inflamed nerves are laying the groundwork for arthritis? Let's dive deep into this interplay between nerves and arthritis, exploring what it means for you.
Understanding Pain: What's Behind Inflammation?
Pain—sharp, dull, chronic, or acute—is an unwelcome guest in anyone’s life. Inflammation is often the silent culprit behind many pain-related conditions. But how does inflammation interact with nerves to contribute to arthritis? Before we tackle this question, it’s essential to explore the broader landscape of inflammation and its role in the body.
The Role of Inflammation
Inflammation is a natural response of your body’s immune system. When faced with injury or infection, inflammation acts as an alarm, summoning immune cells to the affected area to start the healing process. Typically, this is beneficial and part of the body's defense mechanism. However, when inflammation becomes chronic, it can lead to various disorders, including arthritis.
Types of Inflammation
- Acute Inflammation: A short-term reaction, like the swelling experienced after a sprain.
- Chronic Inflammation: Long-lasting and often occurring without injury or infection, which can lead to more severe health issues.
In the context of arthritis, inflammation may persist, wearing down tissues over time and causing joint pain and stiffness.
Arthritis Unpacked: What Are Its Types?
Arthritis isn’t a one-size-fits-all condition but a broad term that encompasses over 100 different types of joint-related diseases. Let's delve into some of the more common forms.
Osteoarthritis vs. Rheumatoid Arthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA): Often referred to as wear-and-tear arthritis, OA results from the breakdown of cartilage in the joints. It's more prevalent among older individuals due to age-related degeneration.
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): An autoimmune disease where the body mistakenly attacks its own tissues, causing persistent inflammation in the joints. RA can affect people of any age and often requires long-term management.
While OA primarily results from mechanical wear, RA is deeply rooted in inflammation.
The Connection Between Nerves and Arthritis
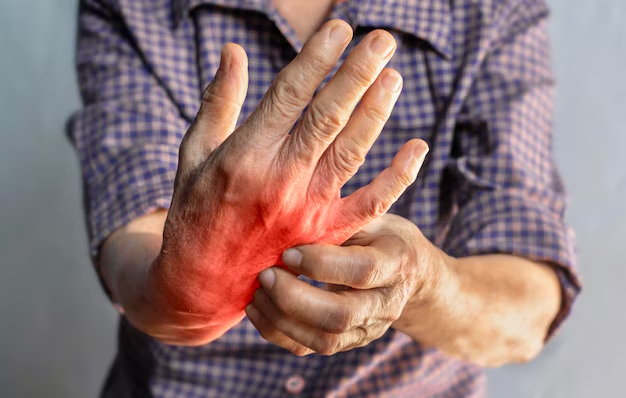
Can an inflamed nerve cause arthritis? Not directly. However, inflamed nerves can amplify the symptoms associated with arthritis, leading to increased pain and reduced mobility.
How Inflamed Nerves Affect Arthritis Symptoms
To understand how inflamed nerves can affect arthritis, we must first consider the role of nerves in our body.
Nerves and Their Functions
Nerves act as the body's communication lines, transmitting signals from the brain to different parts of the body and vice versa. They facilitate movement, sensation, and pain perception.
Nerve Inflammation Consequences
- Increased Pain Perception: When nerves become inflamed, they can send exaggerated pain signals to the brain, intensifying the discomfort associated with arthritis.
- Diminished Mobility: Inflamed nerves can lead to muscle weakness or spasms, making movement more challenging for those dealing with joint issues.
- Heightened Sensitivity: Even light touches or movements can feel painful, compounding the effects of arthritis.
It's easy to see how inflamed nerves and arthritis can create a vicious cycle, with each exacerbating the other's symptoms.
Related Conditions and Comorbidities
There's growing interest and research into how related conditions might intertwine and affect each other.
Fibromyalgia and Arthritis
Fibromyalgia is characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain, often accompanied by fatigue, sleep, and mood disorders. Research suggests that both fibromyalgia and arthritis can co-exist, influencing each other's severity.
- Overlapping Symptoms: Patients commonly experience joint stiffness and pain, akin to arthritis, complicating diagnosis and treatment.
- Nerve Sensitivity: As with arthritis, nerve-related issues in fibromyalgia can exacerbate pain and discomfort.
Understanding these overlaps aids in better management strategies, ensuring comprehensive care for those affected.
Managing Symptoms: Practical Steps Forward
If you suspect that inflamed nerves might be contributing to your arthritis symptoms, there are several non-invasive strategies that might help manage the pain.
Lifestyle Adjustments
- Regular Exercise: Low-impact activities like swimming or cycling can improve joint function and reduce pain.
- Balanced Diet: Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish and flaxseeds, can help minimize inflammation.
- Stress Reduction Techniques: Practices such as yoga or meditation can reduce inflammation by lowering stress levels.
Mind-Body Approaches
- Mindfulness Meditation: Enhances body awareness and can help in managing pain perception.
- Acupuncture: This ancient practice has shown promise in reducing pain by stimulating nerve pathways.
These self-care tactics can be empowering tools in managing joint pain, offering relief without medical intervention.
When to Seek Medical Guidance
While lifestyle changes can offer relief, it's crucial to know when to reach out for professional advice. Persistent or worsening symptoms merit a visit to a healthcare provider.
Recognizing Red Flags
- Unexpected Swelling: If swelling doesn't subside, it could signal further complications.
- Severe and Unrelenting Pain: Pain that disrupts daily activities or sleep should not be ignored.
- Fever or Malaise: Accompanying systemic symptoms may indicate an infection or other underlying issues.
Timely medical consultation ensures you receive a proper diagnosis and the appropriate treatments, avoiding long-term complications.
The Bigger Picture: Interplay of Elements
While inflamed nerves might not directly cause arthritis, their role in influencing pain perception and overall well-being is significant. Recognizing this interplay helps tailor more comprehensive care strategies to manage pain effectively.
Thinking Beyond Pain: Treatment isn't just about mitigating pain but improving quality of life. Recognizing the broader context of nerve involvement in arthritis allows for more holistic approaches that address both body and mind.
Ultimately, by understanding these dynamics, we unlock better ways to manage pain and embrace life with fewer limitations.
Quick Recap & Tips for Managing Arthritis with Nerve Involvement:
- Stay Active! 🚶♂️ Regular low-impact exercises can enhance joint and nerve function.
- Nourish Your Body! 🥗 Incorporate anti-inflammatory foods like omega-3-rich fish.
- Stay Mindful! 🧘🏻♀️ Mindfulness practices can help manage pain sensitivity.
- Be Proactive! 🔍 Seek professional advice if you experience severe or unusual symptoms.
- Embrace Comprehensive Care! 🌟 Exploit the synergy of physical and mind-body strategies for holistic relief.
Related Articles
- Are Bananas Bad For Arthritis
- Are Tomatoes Bad For Arthritis
- Can Arthritis Be Cured
- Can Arthritis Be Reversed
- Can Arthritis Become Septic After Infection From Injection
- Can Arthritis Cause Numbness
- Can Arthritis Cause Swelling
- Can Cracking Knuckles Cause Arthritis
- Can Cracking Your Knuckles Cause Arthritis
- Can Exercise Assist Arthritis Relief
