Can a CT Scan Diagnose Cancer? What You Need to Know
Imagining a world without the looming threat of cancer might seem impossible. But thanks to advancements in medical imaging, detecting cancer early has become more accessible than ever. A pivotal player in this arena is the CT scan. But here's the question that often lingers in people's minds: Can a CT scan definitively diagnose cancer? Let's dive into the world of CT scans to explore their capabilities, limitations, and how they fit into the broader landscape of cancer diagnosis.
Unpacking the CT Scan
What is a CT scan?
A Computed Tomography (CT) scan is a sophisticated imaging technique that employs X-rays to create detailed cross-sectional images of the body's internal structures. Unlike a standard X-ray, which provides a two-dimensional picture, a CT scan offers a 3D view, allowing for a more comprehensive insight into the body's anatomy.
How does a CT scan work?
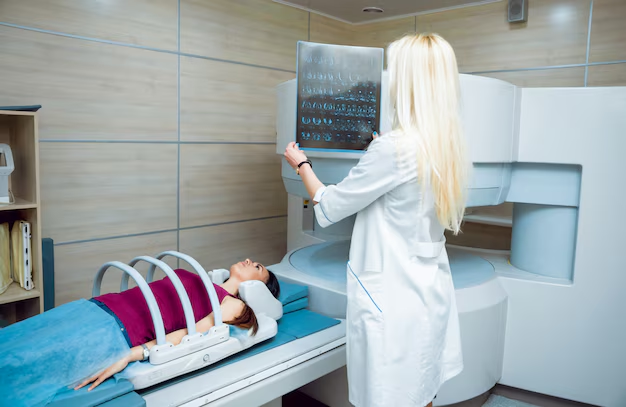
During a CT scan, the patient lies on a motorized table that slides into a doughnut-shaped machine. As the X-ray tube rotates around the body, it captures multiple images from different angles. A computer then processes these images to produce cross-sectional "slices," which offer a detailed view of bones, organs, blood vessels, and other tissues.
Uses of CT scans in medicine
CT scans have a wide range of applications, including:
- Diagnosing injuries: Identifying fractures, internal bleeding, and other trauma.
- Guiding procedures: Assisting in the accurate placement of instruments or treatments.
- Monitoring conditions: Tracking the progress of diseases or the effectiveness of treatments.
- Detecting cancer: Identifying abnormal growths or tumors that might indicate cancer.
Can CT Scans Detect Cancer?
The role of CT scans in cancer detection
CT scans are an essential tool in detecting abnormalities that could suggest the presence of cancer. They can:
- Identify masses and tumors: Detect unusual growths or lesions that might be cancerous.
- Assess the size and shape of tumors: Provide detailed images to evaluate a tumor's dimensions and characteristics.
- Guide biopsy procedures: Help doctors extract tissue samples safely and precisely for further analysis.
However, while CT scans can detect potential cancer indicators, they are not inherently diagnostic. Other tests, such as biopsies and blood tests, are often required to confirm a diagnosis.
Limitations of CT scans in diagnosing cancer
It's crucial to understand that a CT scan alone cannot confirm cancer:
- False positives and negatives: Non-cancerous cells can sometimes appear suspicious, while small, early-stage cancers might not be visible.
- Need for additional tests: A definitive diagnosis typically requires a biopsy, where a tissue sample is examined for cancer cells.
In summary, while a CT scan is a powerful tool for identifying potential cancer, it is typically one piece of the diagnostic puzzle.
Broader Diagnostic Strategies in Cancer Detection
Other imaging techniques
Besides CT scans, various imaging methods play roles in cancer detection:
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Uses magnets and radio waves to create detailed images, useful for soft tissues like the brain and spinal cord.
- PET (Positron Emission Tomography) scans: Explore metabolic activity in tissues and often combined with CT scans for comprehensive results.
- Ultrasound: Utilizes sound waves to visualize structures, commonly used for breast and pelvic examination.
Importance of biopsies
A biopsy remains the gold standard in determining whether a growth is malignant. By extracting a small tissue sample, pathologists can examine cellular structures and confirm the presence of cancer.
Blood tests and markers
Some blood tests can indicate cancer by identifying specific markers produced by cancer cells. These tests, combined with imaging and biopsies, help in forming a comprehensive diagnosis.
Weighing the Pros and Cons of CT Scans
Advantages of CT scans
- Detailed imaging: Superior to standard X-rays, revealing intricate details of the body's internal structures.
- Quick and non-invasive: Generally fast, painless, and doesn't require recovery time post-procedure.
- Widely accessible: Available in many medical facilities and used in various medical fields.
Risks and considerations
- Radiation exposure: CT scans involve higher radiation doses than regular X-rays, though the risk is generally low.
- Allergic reactions: Some patients may react to contrast materials used during the scan.
- Not always definitive: As discussed, additional tests are often necessary to confirm diagnosis.
Understanding When a CT Scan Might Be Recommended
Typical scenarios for CT scans
Doctors may suggest a CT scan under scenarios such as:
- Unexplained symptoms: To investigate unusual or persistent symptoms like weight loss or pain.
- Suspected tumors: When physical exams or initial tests suggest abnormal growths.
- Monitoring existing conditions: To track the status of known cancers or treatment effects.
Preparing for a CT scan
Preparation might involve fasting, avoiding certain medications, or taking specific preparatory steps as advised by healthcare professionals. It's crucial to inform the doctor of any allergies, especially to contrast materials.
Empowering Yourself with Information
Understanding the role of CT scans in diagnosing cancer can empower patients to actively participate in their healthcare journey. By asking informed questions and knowing what to expect, patients can navigate their diagnostic process with greater confidence.
Questions to ask your healthcare provider
- Why is a CT scan necessary in my case?
- What information will this scan provide?
- Are there alternatives or additional tests recommended?
- What precautions should I take for the scan?
The importance of a multidisciplinary approach
A conclusive cancer diagnosis often involves a team of healthcare professionals from various specialties. This collaborative approach ensures comprehensive care and support for patients throughout their journey.
In the fight against cancer, early detection remains a crucial strategy. While CT scans are invaluable tools in identifying potential issues, they are not standalone diagnostic instruments. Combining CT scans with other methods provides a robust framework for diagnosing and subsequently treating cancer efficiently.
Key Takeaways from This Article:
- CT Scans Detect Anomalies 🩻: CT scans play a vital role in spotting abnormal growths and structures indicating potential cancer.
- Not a Standalone Diagnosis 🔍: While powerful, CT scans require confirmation through biopsies and additional tests for a definitive cancer diagnosis.
- Advantages and Risks ⚖️: Quick and informative, CT scans do involve some radiation risks, though benefits often outweigh concerns.
- Questions to Consider 🤔: Empower yourself by asking healthcare providers specific questions about the necessity and outcome of the CT scan.
- Holistic Approach is Key 🌐: A combination of imaging, biopsies, and blood tests, along with professional expertise, ensures comprehensive cancer diagnosis and care.
Related Articles
- Are Breast Cancer Lumps Painful
- Are Chills a Sign Of Cancer
- Are Colon Spasms a Sign Of Cancer
- Are Lytic Lesions Always Cancer
- Are Polyps Cancer
- Can a Blood Test Detect Cancer
- Can a Ct Scan Detect Cancer
- Can a Dexa Scan Show Cancer
- Can a Gastric Emptying Scan Show Cancer
- Can a Lung Biopsy Cause Cancer To Spread
