Understanding Ovarian Cancer Diagnosis: What You Need to Know
Ovarian cancer is often called the "silent killer" due to its subtle symptoms that frequently go unnoticed until the disease progresses. However, understanding how ovarian cancer is diagnosed can empower individuals with crucial knowledge. Whether you're personally affected, supporting a loved one, or simply interested in learning more, this comprehensive guide delves into the diagnostic journey for ovarian cancer, covering every essential aspect with clarity and insight.
Recognizing Early Signs: Why Ovarian Cancer Is Hard to Detect
One of the primary challenges in diagnosing ovarian cancer lies in its early symptoms—or lack thereof. Symptoms are often vague and can be easily confused with common ailments, such as:
- Bloating
- Abdominal pain
- Frequent urination
- Feeling full quickly when eating
While these symptoms can be attributed to various non-serious conditions, persistent or worsening indications warrant further investigation. Understanding this can help expedite a diagnosis, potentially enhancing treatment outcomes.
The Initial Steps: Medical History and Physical Examination
The diagnostic process typically begins with a thorough discussion of one's personal and family medical history. Genetic predispositions, such as a family history of ovarian or breast cancer, can significantly influence the likelihood of developing ovarian cancer. During the appointment, doctors may perform a physical examination, including a pelvic exam, to check for any abnormalities in the ovaries or surrounding areas.
Imaging and Screening: Key Tools for Detection
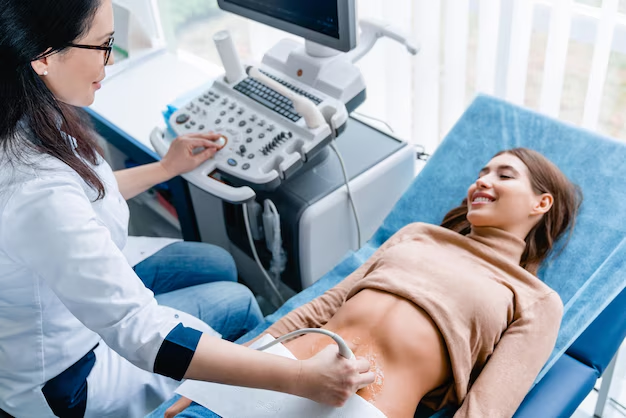
Ultrasound and CT Scans
Imaging tests, such as ultrasounds, play a crucial role in diagnosing ovarian cancer. An ultrasound can help visualize the ovaries and surrounding tissues, revealing any masses or irregularities. Transvaginal ultrasound is particularly effective, providing a closer look at the ovaries.
If an ultrasound indicates abnormalities, doctors might recommend further imaging, like a CT scan or MRI. These allow for detailed cross-sectional images of the abdomen and pelvis and help in assessing the spread of cancer.
CA-125 Blood Test
The CA-125 blood test checks for a specific protein that is often elevated in women with ovarian cancer. While not foolproof (since elevated levels can also occur with other conditions), it remains a valuable tool, particularly in monitoring those already diagnosed with or at high risk for ovarian cancer.
Biopsy: Confirming the Diagnosis
When imaging tests suggest cancer, a biopsy is typically the next step. During this procedure, a sample of ovarian tissue is taken and examined under a microscope to confirm the presence of cancerous cells. This is often the definitive method for confirming ovarian cancer.
How a Biopsy is Conducted
Biopsies can be performed in various ways, depending on the case specifics. Fine needle aspiration and laparoscopy are two common methods. A laparoscopy involves a small incision and is less invasive, often allowing patients a quicker recovery.
Understanding Staging and Grading: Assessing the Extent
Once the presence of ovarian cancer is confirmed, the staging and grading process begins.
Staging
Ovarian cancer staging involves determining how far cancer has spread. The FIGO (International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics) system is commonly used, ranging from Stage I (localized) to Stage IV (advanced).
Here's a brief breakdown:
- Stage I: Cancer is confined to the ovaries.
- Stage II: Cancer has spread to nearby pelvic organs.
- Stage III: Cancer has spread to the abdomen.
- Stage IV: Distant spread, such as to the liver or lungs.
Grading
Grading assesses how much cancerous cells differ from healthy cells. This helps predict how quickly the cancer might grow and spread. A lower grade indicates cells that look similar to normal cells, while a higher grade means more abnormal and aggressive cells.
Genetic Testing: Uncovering Hereditary Links
Genetic testing can offer valuable insights, particularly for those with a family history of certain cancers. This testing looks for mutations in genes like BRCA1 and BRCA2, which significantly elevate the risk of ovarian cancer. Knowing one's genetic status can influence treatment decisions and preventative measures.
Considerations for Genetic Testing
- Family History: A strong family history may prompt genetic testing.
- Personal History: A personal history of related cancers can also be a factor.
- Preventive Measures: Information from genetic testing can guide decisions on preventive surgeries or intensified screening protocols.
Navigating the Emotional Impact
Receiving an ovarian cancer diagnosis can be emotionally overwhelming. Understanding available resources and support systems can make a significant difference.
Coping Strategies
- Support Groups: Engaging with others who have similar experiences can offer comfort and valuable insights.
- Counseling: Professional counseling can help individuals and families navigate the complex emotions associated with a cancer diagnosis.
- Educational Resources: Accessing reputable sources of information can empower patients and caregivers, helping them make informed decisions about treatment and care.
Treatment Options and Next Steps
Once diagnosed, discussing treatment options with healthcare providers is crucial. Treatment plans are typically personalized, based on cancer's stage, grade, and the patient's overall health.
Common Treatments
- Surgery: Often the first line of treatment to remove cancerous tissue.
- Chemotherapy: Utilizes drugs to kill cancer cells or stop them from growing.
- Radiation Therapy: Uses high-energy rays to target and destroy cancer cells.
Empowering Your Journey
Understanding the steps involved in diagnosing ovarian cancer can help demystify the experience and equip individuals with the knowledge needed to advocate for their health.
Summary:
- 🔍 Early Detection: Watch for persistent symptoms like bloating and abdominal pain.
- 🛠 Diagnostic Tools: Include ultrasounds, CT scans, and CA-125 blood tests.
- 🔬 Biopsy: Confirms cancer presence by examining tissue samples.
- 📈 Staging and Grading: Determine cancer spread and aggression.
- 🧬 Genetic Testing: Checks for BRCA1/BRCA2 mutations, informing risk prevention.
- 🤝 Emotional Support: Utilize support groups and counseling for coping.
- 💡 Treatment: Surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation as primary treatments.
This guide simplifies a complex topic, ensuring readers grasp essential aspects of ovarian cancer diagnosis without feeling overwhelmed.
Related Articles
- Are Breast Cancer Lumps Painful
- Are Chills a Sign Of Cancer
- Are Colon Spasms a Sign Of Cancer
- Are Lytic Lesions Always Cancer
- Are Polyps Cancer
- Can a Blood Test Detect Cancer
- Can a Ct Scan Detect Cancer
- Can a Dexa Scan Show Cancer
- Can a Gastric Emptying Scan Show Cancer
- Can a Lung Biopsy Cause Cancer To Spread
