How to Tell if You Have an Ear Infection: Symptoms, Causes, and Next Steps
Ear infections can be a real pain—quite literally. But how can you be sure that what's going on in your ear is an infection? Pinning down the symptoms of an ear infection can sometimes be tricky, especially since the symptoms can vary depending on the type of infection and the age of the person affected. Let’s break it down so you know what to look for and when it might be time to see a healthcare professional.
Recognizing the Signs of an Ear Infection
Common Symptoms
Ear Pain or Discomfort: Often the first sign of trouble. This can range from mild discomfort to sharp, stabbing pain. The pain might come and go, or it might be consistent.
Hearing Loss: Sounds may seem muffled or distant. This happens because fluid build-up behind the eardrum can reduce the ear’s ability to conduct sound.
Drainage from the Ear: While this isn't always present, an ear infection can sometimes cause fluid or pus to seep from the ear, indicating a rupture in the eardrum.
Fever: Especially common in children, a fever can accompany an ear infection as the body responds to the infection.
Headache: The pain from an ear infection often radiates to other parts of the head, causing headaches.
Balance Issues: The ear plays a crucial role in maintaining balance. Infections can disrupt this system, leading to dizziness or unsteadiness.
Symptoms in Children vs. Adults
- Children: They might exhibit irritability, tugging at their ears, trouble sleeping, crying more than usual, and a lack of response to quiet sounds.
- Adults: They may experience more generalized symptoms like earache and pressure, along with subtle hearing changes.
When Symptoms Persist
If symptoms persist or worsen, it's important to seek medical evaluation. Persistent or severe symptoms could indicate a more serious condition requiring professional treatment.
Types of Ear Infections
Understanding the type of ear infection is crucial for recognizing symptoms effectively:
Otitis Media
This is an infection of the middle ear and is one of the most common types of ear infections, especially in younger children. It often follows a cold or respiratory infection.
Otitis Externa
Also known as 'swimmer's ear', this infection affects the outer ear canal. Symptoms often include itchiness in the ear canal, redness, and in some cases, discharge.
Inner Ear Infection
Although less common, inner ear infections can lead to severe dizziness and balance issues. They are more complex and often hardest to diagnose due to overlapping symptoms with other conditions.
Causes and Risk Factors of Ear Infections
Ear infections can be triggered and influenced by several factors:
Common Causes
- Bacterial or Viral Infections: These are the most common causes, often following an upper respiratory infection.
- Allergies: They can cause swelling and fluid build-up, making the ears more susceptible to infection.
- Blockages in the Eustachian Tubes: When these tiny passageways become swollen or clogged, fluid builds up, creating an environment for infection.
Risk Factors
- Age: Younger children are more prone due to their shorter and more horizontal Eustachian tubes.
- Season: Ear infections often occur during winter or cold seasons in conjunction with more frequent coughs and colds.
- Air Quality: Exposure to tobacco smoke or high levels of pollution can increase the likelihood of ear infections.
- Feeding Practices: Bottle-feeding while lying down can introduce bacteria into the middle ear.
Understanding these causes and risk factors can help in taking preventative measures to minimize recurrence or severity of symptoms.
What to Do if You Suspect an Ear Infection
Monitoring Symptoms
Keep track of symptoms, noting their onset, frequency, and severity. This will help provide accurate information to your healthcare provider.
When to Seek Medical Attention
- If you experience severe ear pain, drainage, or balance issues
- If symptoms persist more than 48 hours
- If there's a high fever accompanying ear discomfort
Potential Diagnostic Tests
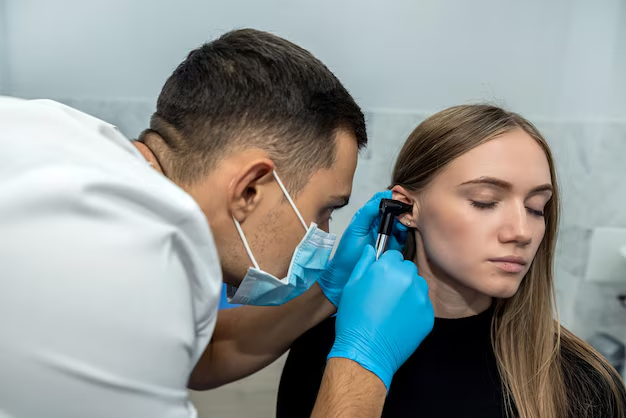
A healthcare provider may perform a physical examination using an otoscope. In some cases, further tests may include hearing tests or tympanometry to assess the presence of fluid behind the eardrum.
Steps for Relief
While it's important to consult a professional for diagnosis and treatment, some general measures can offer relief:
Home Care Tips
- Warm Compresses: Applying a warm cloth to the affected ear can alleviate discomfort.
- Over-the-counter Pain Relievers: Medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage pain.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of fluids can aid in recovery, especially when combating a related respiratory infection.
- Elevate Head while Sleeping: This helps with drainage and eases pressure buildup in the ear.
Preventative Measures
- Reduce Exposure to Tobacco Smoke: Protect against this known irritant which exacerbates ear conditions.
- Manage Allergens: Allergies can contribute to fluid buildup; keeping them under control can help.
- Practice Good Hygiene: This includes proper cleaning of ears and avoiding the insertion of foreign objects into the ear canal.
Summary Table: Identifying and Managing Ear Infections
| Indicator | Description | Tips for Relief |
|---|---|---|
| 👂 Pain or Discomfort | Mild to severe ear pain | Warm Compresses to soothe discomfort |
| 🔊 Hearing Loss | Muffled or distant hearing | Consult a Professional if persistent |
| 💧 Ear Discharge | Fluid or pus from the ear | Seek Medical Attention for proper evaluation |
| 🌡️ Fever | Accompanying symptom, common in children | Use Over-the-Counter Medications like ibuprofen |
| 🚶 Balance Issues | Dizziness or unsteadiness | Avoid Sudden Movements, remain seated or lying down |
By understanding the nuances of ear infections and observing clear signs and symptoms, you empower yourself to take informed steps towards relief and recovery. Awareness and careful monitoring are your best tools in managing your ear health effectively.
Related Articles
- Are Ear Infections Contagious
- Can Adults Get Ear Infections
- Can Amoxicillin Treat Ear Infections
- Can An Ear Infection Cause a Sore Throat
- Can An Ear Infection Cause Diarrhea
- Can An Ear Infection Cause Head Pain
- Can An Ear Infection Cause Jaw Pain
- Can An Ear Infection Cause Teeth To Hurt
- Can An Ear Infection Cause Vomiting
- Can An Ear Infection Heal On Its Own
