Understanding Leukemia: From Symptoms to Diagnosis
When faced with health concerns, knowing what to expect can significantly ease the anxiety associated with medical diagnoses. Given the complexity of conditions such as leukemia, a foundational understanding of the diagnostic process is invaluable. This article aims to guide you through the journey of diagnosing leukemia, offering insights into symptoms, diagnostic methods, and what each step entails.
Unmasking Leukemia: What Are The Symptoms?
Before delving into how leukemia is diagnosed, it’s essential to recognize its symptoms. Leukemia, a cancer of the blood and bone marrow, can be sneaky in its presentation. Understanding that symptoms may vary and can be mistaken for less severe illnesses is crucial.
Common Symptoms
- Persistent Fatigue: A profound and lasting tiredness that doesn’t improve with rest.
- Frequent Infections: Due to the decreased production of healthy white blood cells, the body’s ability to fight infections is hampered.
- Easy Bruising or Bleeding: Including nosebleeds or bleeding gums, because of a low platelet count.
- Bone or Joint Pain: As the abnormal cells accumulate, they can cause pressure and pain in the bones.
- Swollen Lymph Nodes: Typically painless, these may be found in the neck, armpit, or groin.
- Paleness and Shortness of Breath: Resulting from anemia due to a reduced number of red blood cells.
The Diagnostic Pathway: How Is Leukemia Identified?
Recognizing symptoms is just the first step. The pivotal task is confirming a leukemia diagnosis through specific tests and examinations. Each diagnostic method plays a unique role in painting the full picture.
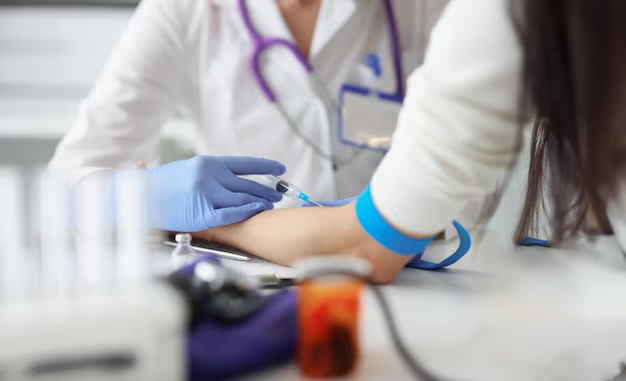
1. Complete Blood Count (CBC) Test
The CBC test is often the first step when leukemia is suspected. This test measures the number of white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets in the blood. Signs of leukemia in a CBC might include:
- Abnormal levels of white blood cells
- Low red blood cell count (anemia)
- Decreased platelets
Note: While a CBC can indicate the potential presence of leukemia, it cannot confirm the diagnosis alone.
2. Bone Marrow Aspiration and Biopsy
The definitive method for diagnosing leukemia involves examining the bone marrow.
- Bone Marrow Aspiration: Involves extracting a small amount of liquid marrow.
- Biopsy: Removes a small solid piece of bone marrow tissue.
Key Takeaway: This procedure helps confirm the presence of leukemia cells and assists in determining the type of leukemia, which is essential for creating a treatment plan.
3. Cytogenetic Analysis
Looking at the chromosomes in cells from blood or bone marrow samples can reveal specific changes. Chromosomal abnormalities are common in leukemia and can guide treatment options. This process often includes:
- Karyotyping: Visualizing the complete set of chromosomes to identify changes.
- Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH): A more precise technique to detect specific genetic abnormalities.
4. Flow Cytometry and Immunophenotyping
These tests analyze proteins on the surface of leukemia cells. By recognizing these proteins, doctors can accurately classify the type of leukemia, which is vital for targeted treatment strategies.
5. Molecular Testing
Advanced tests such as Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) can detect genetic mutations or changes in the leukemia cells. This step is particularly important for personalizing treatment plans and assessing prognosis.
Navigating the Diagnosis: What Does Each Result Mean?
Interpreting test results can be overwhelming. Understanding what each result signifies can help demystify the process.
Analyzing Blood Counts
- High White Blood Cell Count: Often indicates an overproduction of abnormal leukemic cells.
- Low Platelets and Red Blood Cells: Suggests bone marrow failure, a hallmark of leukemia.
Examining Bone Marrow
- Presence of Leukemia Cells: Confirms diagnosis.
- Subtype Identification: Guides prognosis and treatment planning, crucial for deciding between chemotherapy, targeted therapy, or bone marrow transplantation.
The Significance of Genetic and Protein Markers
- Chromosomal Changes: Provide clues on leukemia’s aggressiveness and potential response to treatment.
- Protein Markers: Directly influence treatment modalities, including the use of monoclonal antibodies or targeted therapies.
Beyond Diagnosis: Embracing the Journey Ahead
Receiving a leukemia diagnosis is just the beginning. It opens the door to a journey filled with treatment decisions, emotional processing, and a hopeful path toward remission.
Treatment Approaches
Depending on the leukemia type and individual characteristics, treatment may involve:
- Chemotherapy: The primary treatment to kill leukemia cells.
- Targeted Therapy: Uses drugs that specifically target abnormalities in cancer cells.
- Radiation Therapy: To destroy cancer cells or shrink lymph nodes.
- Bone Marrow Transplantation: Replaces diseased bone marrow with healthy cells.
- Immunotherapy: Boosts the body’s natural defenses to fight off leukemia.
Emotional and Practical Support
Understanding a leukemia diagnosis impacts more than just the physical body. Emotional health and practical adjustments are equally important.
- Access to Support Groups: Provides a community of others sharing similar experiences.
- Mental Health Care: Seeking counseling or therapy can be beneficial.
- Financial and Logistical Planning: Navigating healthcare insurance, treatment costs, and work-life balance are pivotal.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
Post-diagnosis, continuous monitoring is crucial for adapting treatment strategies and ensuring remission. Regular blood tests and imaging help track progress and any signs of recurrence.
Embracing Knowledge as Power
Knowledge is empowering when navigating a leukemia diagnosis. Being informed about symptoms, diagnostic processes, and potential treatment paths provides the confidence to engage in conversations with healthcare providers, ensuring a proactive role in health management. Facing leukemia involves uncertainty, but the wealth of information and resources available promises hope and support at every step.
📌 Summary at a Glance
- 🔍 Recognize Symptoms: Fatigue, frequent infections, and bruising are common signs.
- 📝 CBC Tests: Detects abnormal blood cell levels suggesting leukemia.
- 🔬 Bone Marrow Tests: Confirm diagnosis and help identify leukemia type.
- 🧬 Genetic Analysis: Guides treatment options with chromosomal insights.
- 💊 Treatment Pathways: Include chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and more.
- 👐 Holistic Support: Integrates emotional, financial, and social resources.
- 🔄 Ongoing Monitoring: Crucial for ensuring remission and managing healthcare.
Understanding the pathway from suspicion to diagnosis is a vital component of managing and overcoming leukemia. With knowledge as a tool, facing this challenge becomes a well-navigated journey.
Related Articles
- Can Leukemia Be Cured
- How Do Cats Get Feline Leukemia
- How Do They Test For Leukemia
- How Do You Get Leukemia
- How Do You Test For Leukemia
- How High Are Monocytes In Leukemia
- How Is Feline Leukemia Spread
- How Is Feline Leukemia Transmitted
- How Is Leukemia Diagnosed
- How Long Can You Live With Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
