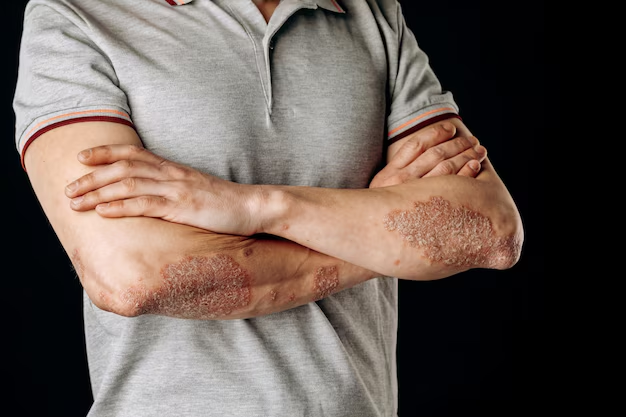
Understanding Shingles: What Triggers This Common Disease?
Imagine waking up one day to find a painful rash forming on your body, not knowing what caused it or how long it will last. For many, this is the reality of shingles, a condition baffling in its sudden onset and troublesome symptoms. In this article, we unravel the mystery of what brings on shingles, highlighting the risk factors, symptoms, and preventive measures. Our aim is to provide clear, engaging information to help you understand this condition better.
Unraveling Shingles: The Basics
Shingles, known medically as herpes zoster, is an infection caused by the reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus, the same virus responsible for chickenpox. Most people contract chickenpox during childhood, which the immune system eventually overcomes. However, the virus remains dormant in the body's nerve tissue, sometimes for decades, until it reawakens as shingles.
Key Symptoms of Shingles
- Painful Rash: Often resembling a stripe wrapping around one side of the body.
- Blisters: Fluid-filled and can burst, creating crusted sores.
- Pain And Tingling: OccURing days before the rash appears.
- Fever And Chills: Accompany the rash in some cases.
These symptoms render shingles not only uncomfortable but potentially debilitating for the duration it persists.
What Brings On Shingles?
1. Age: A Natural Risk Factor
The Natural Aging Process decreases immune efficiency, making older adults more susceptible to the reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus. Shingles is most common in individuals over 50, although it can occur at any age.
2. Compromised Immune System
A weakened immune system is a prominent trigger for shingles. Various factors can lead to immune deficiencies, including:
- Medical Conditions: Diseases such as HIV/AIDS or cancer.
- Medications: Immunosuppressive drugs for conditions like arthritis or after organ transplants.
These conditions reduce the body's ability to keep the varicella-zoster virus in check.
3. Stress: An Underestimated Trigger
Chronic stress creates physical strain, lowering immune defense and potentially triggering the reactivation of the virus. High cortisol levels, a stress hormone, can suppress immune function, paving the way for a shingles outbreak.
4. Physical Trauma
Injuries or physical traumas, especially near the site where the virus is lying dormant, can trigger its activation.
Prevention and Management
Vaccination: Your First Line of Defense
One of the best preventive measures against shingles is vaccination. The shingles vaccine is recommended for adults over the age of 50, significantly reducing the risk of developing the disease and mitigating the severity if it does occur.
Lifestyle Adjustments for Lower Risk
Implementing healthier lifestyle choices can reduce the risk factors associated with shingles:
- Balanced Diet: Rich in vitamins and minerals to support immune health.
- Regular Exercise: Enhances overall well-being and immune function.
- Stress Management Techniques: Practices like yoga, meditation, and regular breaks to alleviate stress.
Self-care During An Outbreak
Shingles requires careful management to minimize discomfort and prevent complications. Some self-care strategies include:
- Cool Compresses: For soothing relief.
- Loose Clothing: To avoid irritating the rash.
- Regular Hygiene: Keeps the rash clean and reduces the risk of infection.
Complications: When Shingles Becomes More Serious
While shingles often resolves without major issues, complications can arise. These include:
Postherpetic Neuralgia (PHN)
PHN is a chronic pain condition that can persist months or even years after the rash has healed. It's more common among older adults and can significantly impact quality of life.
Vision Loss
If shingles occur near or in the eyes, it can lead to serious complications, including vision loss.
The Emotional and Physical Toll
Beyond the physical symptoms, shingles can also take an emotional toll. Coping with discomfort and potentially lasting effects, such as PHN, might lead to emotional distress. Those affected can benefit from:
- Support Groups: Connecting with others who understand the experience.
- Mental Health Support: Counseling services to manage anxiety or depression associated with the condition.
Closing Thoughts
Understanding what brings on shingles not only helps in prevention but also in managing its outcomes effectively. By recognizing risk factors, acknowledging the symptoms, and taking preventive measures, you can better navigate this condition with confidence and care.
Summary of Key Points:
- Shingles Origin: Reactivation of the dormant chickenpox virus.
- Risk Factors: Age, immune suppression, stress, and physical trauma.
- Prevention: Vaccination, healthy lifestyle, managing stress.
- Care During Outbreak: Cool compresses, loose clothing.
- Potential Complications: PHN, vision loss in severe cases.
- Emotional Support: Key in managing shingles' impact.
🧘♀️ A calm mind is an effective immune booster
💉 Consider vaccination for prevention
🥗 Eat well, stay active to bolster defenses