Understanding Thyroid Problems: What You Need to Know
Have you ever felt an inexplicable fatigue that lingers despite a full night's sleep, or perhaps noticed your weight fluctuating without change in diet or exercise? These symptoms, often dismissed or overlooked, might hint at an underlying issue with your thyroid gland. This small but mighty gland, located in the neck, plays a pivotal role in regulating your body's metabolism, energy production, and even mood. So, how do you know if your thyroid might be the culprit behind these puzzling symptoms? Let's delve into the world of thyroid health and explore how you can recognize potential problems.
Why the Thyroid Matters
Before jumping into symptoms and signs, it's important to grasp why the thyroid is vital. The thyroid gland produces hormones such as thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which influence almost every cell in your body. These hormones regulate your metabolism, affecting how fast or slow your body uses energy. An imbalance in these hormones can lead to significant health issues, ranging from heart problems to mental health conditions.
Types of Thyroid Disorders
- Hypothyroidism: This condition is characterized by an underactive thyroid gland that doesn't produce enough hormones. It's often associated with fatigue, weight gain, and depression.
- Hyperthyroidism: Conversely, this involves an overactive thyroid that produces excess hormones, leading to symptoms like weight loss, anxiety, and a rapid heartbeat.
- Thyroiditis: Inflammation of the thyroid, which can cause temporary disruptions in hormone production.
- Nodules and Goiter: Some may develop lumps or swelling in the thyroid, potentially affecting hormone production or indicating a more serious condition.
Recognizing the Signs of Thyroid Trouble
To address the question of how to know if you have thyroid problems, let's break down the common signs and symptoms you might experience.
Symptoms of Hypothyroidism
- Fatigue: Persistent exhaustion is a hallmark of an underactive thyroid.
- Weight Gain: Unexplained weight increase, even with normal food intake and physical activity levels.
- Cold Sensitivity: A constant feeling of coldness is common, even in warm environments.
- Hair and Skin Changes: Dry skin and brittle hair or nails may indicate hypothyroidism.
- Cognitive Issues: "Brain fog," or difficulty concentrating, could be related to thyroid issues.
- Depression and Mood Swings: Shifts in mood or feelings of depression without a clear cause.
Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism
- Unintended Weight Loss: Losing weight without trying often points to an overactive thyroid.
- Increased Appetite: Paradoxically, while losing weight, you might feel hungrier than usual.
- Elevated Heart Rate: A noticeably fast heartbeat, sometimes accompanied by palpitations.
- Anxiety and Irritability: Heightened nervousness or irritability are common hyperthyroid symptoms.
- Sweating and Heat Sensitivity: Excessive sweating and discomfort in hot temperatures.
- Tremors: Slight shaking, usually in the hands or fingers.
Physical Indicators
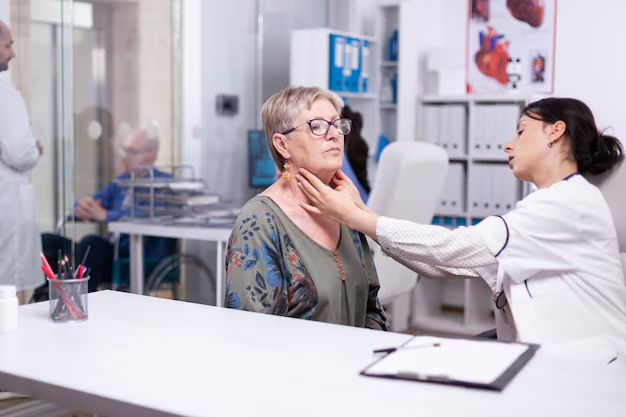
- Neck Swelling: Enlargement of the thyroid gland, known as a goiter, may become visible or palpable.
- Eye Changes: In conditions like Graves' disease, bulging eyes or vision changes can occur.
What Causes Thyroid Disorders?
Understanding what causes thyroid issues can empower you to take preemptive measures or engage in informed discussions with healthcare providers.
Common Causes
- Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions like Hashimoto's thyroiditis or Graves' disease involve the immune system attacking the thyroid.
- Iodine Deficiency: Iodine is critical for thyroid hormone production; a deficiency can lead to hypothyroidism.
- Genetic Factors: If thyroid problems run in your family, your risk is higher.
- Stress Levels: Chronic stress impacts hormonal balance and can contribute to thyroid dysfunction.
- Certain Medications: Some drugs may interfere with thyroid hormone production or function.
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
- Dietary Choices: Diets low in iodine or high in goitrogens (like those found in soy and cruciferous vegetables) can influence thyroid health.
- Radiation Exposure: Particularly in the neck area, this can damage thyroid cells over time.
Seeking Diagnosis and Understanding Tests
If symptoms align with those mentioned, it might be wise to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis.
Diagnostic Steps
- Physical Examination: A doctor may check for neck swelling and discuss symptoms.
- Blood Tests: Measurement of hormone levels, such as Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) and free T4, offers insights into thyroid activity.
- Imaging Tests: Ultrasounds and radioactive iodine uptake tests can evaluate the gland's structure and function.
- Biopsies: If nodules are detected, a fine-needle aspiration biopsy may be conducted to rule out cancer.
Living with a Thyroid Disorder
Managing thyroid disorders requires a combination of medical intervention and lifestyle adjustments.
Medical Approaches
- Medication: Synthetic hormone replacement for hypothyroidism or medications to inhibit hormone production for hyperthyroidism.
- Surgery: In cases of large goiters or cancerous nodules, surgical removal of the thyroid might be necessary.
- Radioactive Iodine: This treatment for hyperthyroidism helps reduce thyroid hormone production.
Lifestyle Considerations
- Nutrition: Ensuring adequate iodine intake and balancing nutrients can support thyroid health.
- Regular Exercise: Helps combat symptoms like fatigue and weight gain.
- Stress Management: Practices such as yoga or meditation can maintain hormonal balance.
- Routine Monitoring: Regular check-ups and blood tests are essential for adjusting treatment plans.
Support and Resources
- Join Support Groups: Engaging with others who have similar conditions can provide emotional support and practical advice.
- Stay Informed: Keeping up to date on thyroid research and treatments empowers proactive health management.
Understanding and recognizing thyroid issues can significantly affect your quality of life. By paying attention to your body's signals and seeking professional evaluation when needed, you can take charge of your health journey.
🌟 Quick Reference Guide
Watch for Symptoms:
- Hypothyroidism: Fatigue, weight gain, cold sensitivity
- Hyperthyroidism: Weight loss, rapid heartbeat, anxiety
Know Risk Factors:
- Autoimmune diseases, iodine deficiency, family history
Seek Professional Diagnosis:
- Blood tests, physical exams, imaging
Lifestyle Strategies:
- Balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management
Stay Connected:
- Support groups and credible health resources
Empower yourself by understanding the thyroid, its functions, and how to recognize and manage potential problems. 🌿
Related Articles
- Can a Man Have a Thyroid Problem
- Can Taneringe Juice Make Thyroid Pil Absorption Faster
- Can Thyroid Cause Weight Gain
- Can Thyroid Eye Disease Be Cured
- Can Thyroid Issues Cause Hair Loss
- Can Thyroid Issues Cause Headaches
- Can Thyroid Medication Cause Brown Spots On Skin
- Can Thyroid Nodules Cause Mucus In Throat
- Can u Live Without Thyroid
- Can You Live Without a Thyroid
