Understanding the Thyroid Gland: Location, Function, and Importance
When understanding our bodies, some might overlook the small but mighty thyroid gland. Its unassuming stature often belies its immense responsibility in regulating various bodily functions. Let's dive into the thyroid gland's location, see why it's vital, and explore related topics that add context and clarity to this crucial part of human anatomy.
What is the Thyroid Gland?
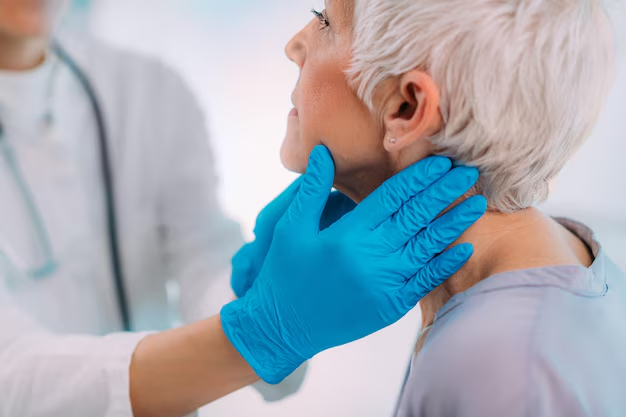
The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped organ situated in your neck, just below your Adam's apple. Despite its small size, it's one of the most significant glands in the endocrine system. This gland's primary function is to produce hormones that regulate the body's energy use, control metabolism, and influence growth and development.
Location: Where Exactly Is It?
Positioning in the Neck:
As mentioned, the thyroid is located in the neck. Specifically, it wraps around the trachea, more commonly known as the windpipe. It's nestled just above the collarbone and below the larynx (voice box), making it relatively accessible for medical examinations.
Anatomical Structure:
The gland consists of two lobes (right and left) connected by a small bridge of tissue called the isthmus. This configuration resembles a butterfly, hence the gland's nickname. On either side of the windpipe, you can find these lobes expanding slightly upward and downward, helping the gland maintain its pivotal role in the neck.
Function: Why Is the Thyroid Important?
Hormone Production:
The thyroid gland produces several critical hormones, most notably thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which are essential for controlling the speed of your metabolism—how your body uses energy. T3 and T4 production is regulated by thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), which your pituitary gland releases.
Impact on Bodily Systems:
- Metabolism Regulation: Thyroid hormones influence the rate at which calories are burned, affecting weight management and body heat.
- Growth and Development: Particularly in children, these hormones ensure proper growth and development.
- Heart and Digestive Function: The thyroid plays a role in maintaining heart rate and aiding digestion by stimulating movements in the digestive tract.
- Brain Development: Thyroid hormones are also vital for brain development, especially in pregnant women and newborns, influencing cognitive abilities and neurological function.
Common Thyroid Disorders
Understanding where the thyroid gland is and what it does helps in identifying common thyroid disorders. Recognition of these disorders can prevent future health complications.
Hypothyroidism: Underactive Thyroid
Symptoms:
- Fatigue
- Weight gain
- Cold intolerance
- Depression
- Dry skin and hair
Hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid doesn't produce enough hormones, slowing down bodily functions. While it can affect anyone, middle-aged women are more prone to this condition.
Hyperthyroidism: Overactive Thyroid
Symptoms:
- Rapid heartbeat
- Weight loss
- Increased appetite
- Nervousness or anxiety
- Heat intolerance
Hyperthyroidism arises when the thyroid produces too much hormone, accelerating metabolic processes. The condition can lead to significant health issues if not managed properly.
Other Thyroid Issues
- Thyroid Nodules: These are lumps within the thyroid gland, often benign but occasionally indicative of thyroid cancer.
- Goiter: An enlarged thyroid, which can indicate either hypo or hyperthyroidism.
- Thyroid Cancer: A relatively rare but critical condition that requires medical intervention.
Factors Affecting Thyroid Health
Several elements can influence thyroid health, underscoring the importance of understanding the gland's role and location.
Dietary Influence
Iodine:
Iodine is essential for the production of thyroid hormones. A deficiency can lead to hypothyroidism, while excess iodine can aggravate hyperthyroidism. Consuming iodized salt and seafood can promote thyroid health.
Selenium and Zinc:
These minerals support the conversion of T4 to T3. Brazil nuts (selenium) and meat and shellfish (zinc) are excellent dietary sources.
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
Stress:
Chronic stress can impact the thyroid's functions, emphasizing the importance of stress management techniques, such as exercise, meditation, or yoga.
Smoking and Alcohol:
Both can affect the gland's function and exacerbate symptoms of thyroid disorders. Moderation is key to maintaining thyroid equilibrium.
Genetic and Gender Predisposition
Some thyroid conditions have genetic links, meaning a family history might increase one's risk. Additionally, women are more likely to develop thyroid problems than men, pointing to the necessity of regular screening.
How to Recognize Thyroid Symptoms
Identifying potential thyroid issues early can make a significant difference in management and treatment. Here's how you can recognize symptoms:
- Unexplained Weight Changes: Whether gaining or losing weight without diet changes, this could suggest a thyroid imbalance.
- Mood Fluctuations: Anxiety, depression, or changes in mood might indicate thyroid activity deviations.
- Temperature Sensitivity: A heightened sensitivity to cold or hot temperatures can be thyroid-related.
- Neck Swelling: Visible swelling in the neck or a sensation of something pressing on your throat should not be ignored.
The Importance of Regular Check-Ups
Regular medical check-ups are vital, especially if you have risk factors for thyroid disease. Doctors can perform a simple blood test to measure levels of TSH, T3, and T4. This helps in the early detection and management of thyroid conditions, improving quality of life.
Empowering Yourself with Knowledge
Understanding the thyroid gland's location, function, and potential issues empowers you with the knowledge to manage and maintain your health proactively. It's more than just knowing where the thyroid gland is; it's about recognizing its impact and the importance of keeping it balanced.
By recognizing symptoms early and making informed lifestyle choices, you can ensure your thyroid—and your body—functions optimally. Remember, the thyroid might be small, but its role is anything but minor.
Quick Takeaways 🌟
- Location: The thyroid gland is located in the neck, wrapping around the trachea.
- Function: Produces T3 and T4, regulating metabolism and influencing various bodily functions.
- Common Disorders: Hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, each with distinct symptoms.
- Dietary Needs: Iodine, selenium, and zinc are crucial for thyroid health.
- Detection: Regular check-ups and awareness of symptoms lead to early diagnosis.
- Empowerment: Knowledge of the thyroid's role aids in proactive health management.
By considering these factors and insights, you can strive towards better thyroid health and overall well-being. 🌈
Related Articles
- Can a Man Have a Thyroid Problem
- Can Taneringe Juice Make Thyroid Pil Absorption Faster
- Can Thyroid Cause Weight Gain
- Can Thyroid Eye Disease Be Cured
- Can Thyroid Issues Cause Hair Loss
- Can Thyroid Issues Cause Headaches
- Can Thyroid Medication Cause Brown Spots On Skin
- Can Thyroid Nodules Cause Mucus In Throat
- Can u Live Without Thyroid
- Can You Live Without a Thyroid
