Understanding Diabetes: How It Affects Your Body and Health
The subject of diabetes often comes packed with a lot of questions and concerns about what it means for the millions of people who live with it every day. Whether you're trying to understand the condition for yourself or support someone who has it, the complexities of diabetes can be daunting. However, by breaking it down into manageable parts, you can gain a clearer picture of how diabetes works and what it entails.
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a chronic health condition marked by the body's inability to properly process glucose, a critical energy source for the body's cells. This disruption leads to elevated levels of blood sugar, which can result in a range of health complications.
Types of Diabetes
Before digging deeper, it's important to note the main types of diabetes:
- Type 1 Diabetes: An autoimmune condition where the body attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
- Type 2 Diabetes: This most common form often relates to lifestyle factors, where the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn't produce enough of it.
- Gestational Diabetes: Occurs during pregnancy and can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
How Does Insulin Work?
To comprehend diabetes, one must first understand insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas. Insulin plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels:
- Glucose Entry: Insulin facilitates the entry of glucose into the cells, providing energy for various bodily functions.
- Blood Sugar Regulation: It helps to store excess glucose in the liver, which can be used when the body requires energy between meals.
Without sufficient insulin action, glucose accumulates in the bloodstream, leading to hyperglycemia, a characteristic of diabetes.
The Symptoms of Diabetes
Diabetes may reveal itself through a variety of symptoms, which can vary in intensity and frequency depending on the type and severity:
- Increased Thirst and Urination: High blood sugar levels can cause elevated thirst and an increased need to urinate.
- Fatigue: Insufficient glucose in the cells results in reduced energy.
- Weight Loss: Despite increased hunger, some people experience unintentional weight loss.
- Blurred Vision: Excess blood sugar can affect eye lenses, resulting in temporary blurring.
Recognizing these symptoms early can lead to a prompt diagnosis and management plan, potentially preventing complications.
Diagnosing Diabetes
Diagnosis generally involves a series of blood tests to measure blood glucose levels:
- Fasting Blood Sugar Test: Measures blood sugar after an overnight fast.
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test: Evaluates the body’s ability to manage glucose after ingestion.
- A1C Test: Provides an average blood sugar level over the past two to three months.
These tests help doctors determine whether someone has diabetes, prediabetes, or is managing their condition well.
Managing Diabetes
While there's currently no cure for diabetes, effective management is key. Here are several ways to manage the condition:
Lifestyle and Diet
- Balanced Diet: Eating a well-rounded diet with controlled carbohydrates, ample fiber, and healthy fats is beneficial.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity helps lower blood sugar levels and can improve insulin sensitivity.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the risk of complications, especially in type 2 diabetes.
Medication
- Insulin Therapy: Necessary for type 1 diabetes and sometimes used in advanced type 2 diabetes.
- Oral Medications: Often prescribed for type 2 diabetes to improve insulin sensitivity or reduce glucose production in the liver.
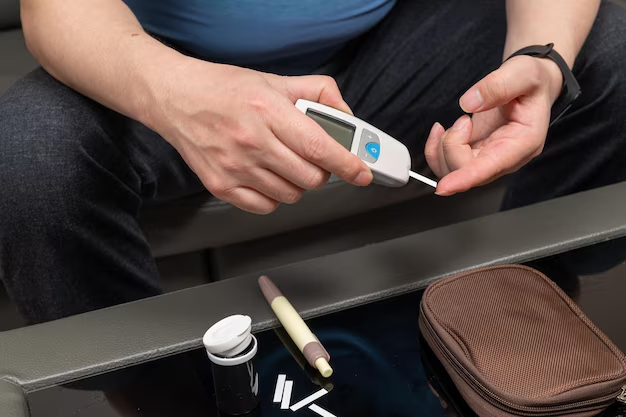
Monitoring
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels enables individuals to make informed decisions about diet, activity, and medication adjustments.
Preventing Diabetes Complications
Diabetes requires vigilant management to prevent complications that could affect the eyes, kidneys, heart, and nerves:
- Eye Health: Regular screenings to detect and treat retinopathy early.
- Kidney Function: Blood pressure and blood sugar control play a big role in reducing kidney disease risk.
- Cardiovascular Care: Monitoring cholesterol and blood pressure and adopting heart-healthy lifestyle habits.
- Foot Care: Preventative care and monitoring to avoid infections and ulcers.
Quick actions and regular check-ups can significantly mitigate the longer-term complications associated with diabetes.
Living with Diabetes
People with diabetes can live fulfilling lives by understanding and managing their condition effectively:
- Education and Support: Participating in diabetes education programs can empower individuals with knowledge and self-care skills.
- Building a Support Network: Whether it involves friends, family, or support groups, connectivity plays a significant role in managing emotional and psychological challenges.
- Setting Realistic Goals: Setting achievable wellness and health goals ensures sustainable progress and motivation.
Summary Section
Key Takeaways on Managing Diabetes
- 🧠 Understanding: Deepen your understanding of diabetes types—each comes with its unique challenges and management strategies.
- 🍎 Lifestyle Choices: Focus on balanced diets and regular exercise to manage blood sugar levels effectively.
- 💉 Medication: Utilize medications as prescribed to augment lifestyle changes and control blood glucose levels.
- 🔍 Regular Monitoring: Stay consistent with monitoring to prevent complications and adjust treatment plans as necessary.
- 🤝 Support: Lean on educational resources and support networks for guidance and encouragement.
Embracing Individual Journeys
Diabetes does not define you; it's a component of your overall health picture. Empower yourself with knowledge and supportive habits to lead a vibrant and active life despite the condition. The key lies in continuous learning, adapting strategies that fit your lifestyle, and maintaining a positive outlook on your health journey.